Engineering Career Ladder
A simple and effective engineering career ladder template for CTOs and engineering managers to grow, promote, and evaluate software engineers.
TL;DR: A practical engineering career ladder template with dual progression tracks (management and senior engineer), role-based accountability, and structured promotion processes for startups with 10-50 engineers.
Many CTOs and engineering managers struggle with career development when they reach around 10 engineers. At that point some engineers have been with the company for a while and demand a promotion. Because they fear chaos, CTOs are looking for a career framework. While there are many out there, most are too complex and created for big companies. They overwhelm engineers and are not helpful as guidance.
Why?
Why would you define a career ladder? Perhaps you’re a non mainstream organization and don’t need one. Perhaps you don’t have the problems of others, so you don’t need one. Many CTOs though need a career ladder at one point in growing their team:
- Some people define themselves by explicit title progression
- A defined career ladder and salary/promition process reduces politics
- Everyone knows how it works and what to expect
- Easier for you to manage, hold people accountable and make them own things and take responsibility
- Makes your engineering manager job easier
What about the ladders out there?
There are many ladders out there. Most of them are to big, they might have more steps than you have engineers. They are fine, they work for large companies. But they don’t work for you if you have 10-50 engineers.
Example that works
Here is a simple example that works. You start with interns, then juniors up to a tech lead. The tech lead is half-way a manager without people management responsibilities.
At that point the career ladder splits into two tracks:
- Management track
- Senior engineer track
For many startups it’s better that seniors and tech leads chose the management track - first because depending on your planned org structure you need team leads and engineering managers. Second because you need to have work for staff engineers and principals. If everyone wants to become a staff engineer, your organization needs to be able to deal with this.
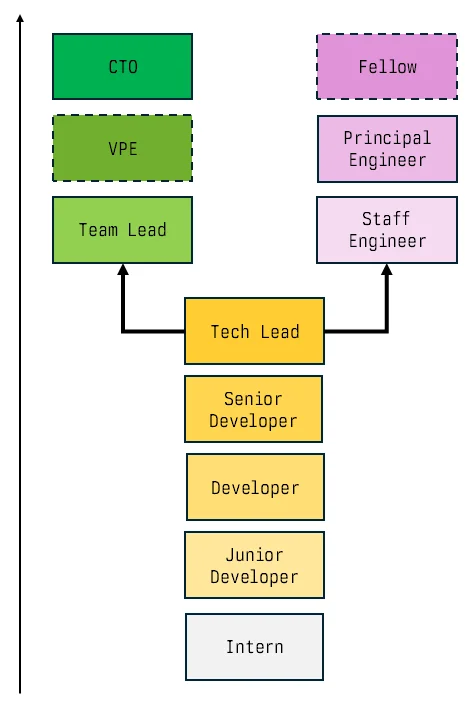
The IC roles:
- Intern
- Junior
- Developer
- Senior
- Tech Lead
Then we split into a management track:
- Team Lead
- Engineering Manager
- VP of Engineering
- CTO
And a senior engineer track:
- Staff Engineer
- Principal Engineer
- Fellow Engineer
Basically the same Y-ladder can be applied to QA, Devops and Data.
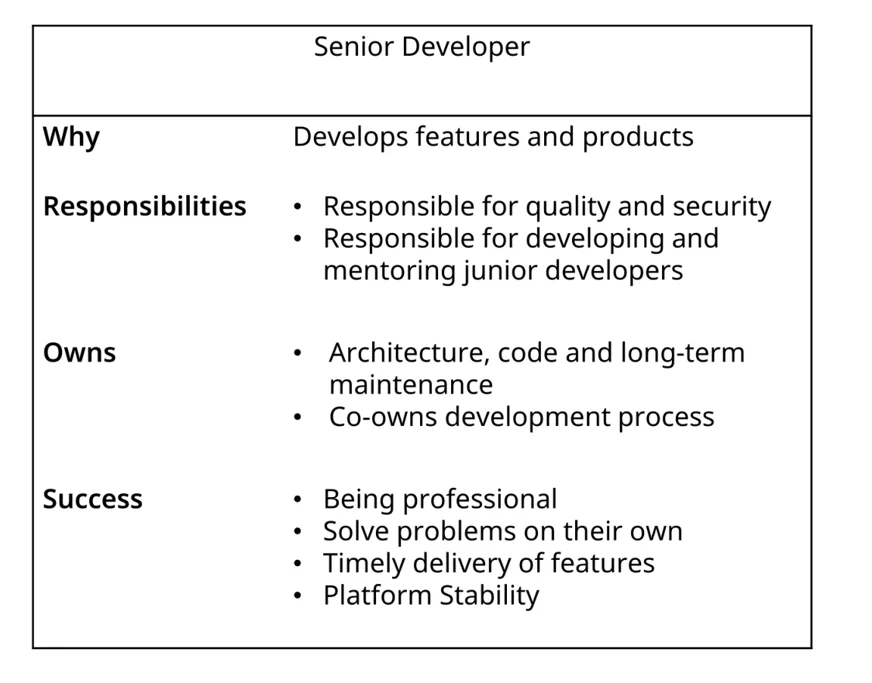
Role descriptions
Every role needs a role description. A role description gives guidance to the employee and tells them what is expected of them.
Based on role descriptions you can:
- Talks about salary
- If the individual fulfils the role or exceeds the role, they should be in the upper quarter of the salary range. If they underpeform to their role description, they are in the lower quarter of the salary range.
- Talks about promotion
- First step to promotion is fulfilling their current role. If you agree that they are ready for the next role, you can start the promotion process. You can take a look at the next role description and see if they are ready for it, what already works, what gaps they need to close. When they fulfil 80% of the next role description, you can promote them.
- Performance management
- Holding people accountable and talk about their performance only works with proper role descriptions in place. Role descriptions are build around ownership and responsibilities.
Promotions
When do you promote someone? When they fulful or exceed their current role and the company has a (future) need for the next role.
Promotions need to be a constant topic in 1:1s. Not every 1:1 but developers should know if they are on the right track. If they are, tell them about a possible promotion - or encourage them. They might also come to you with a promotion request.
First step to promotion is fulfilling their current role. If you agree that they are ready for the next role, you can start the promotion process. You can take a look at the next role description and see if they are ready for it, what already works, what gaps they need to close. When they fulfil 80% of the next role description, you can promote them.
Gaps are between their current role and the next role - with proper role descriptions in place it’s easy to identify them. Never promote on years-of-experience or how long they have been with the company.
Gaps can be closed by:
- Managing projects
- Presenting to the board
- Managing architecture decisions
- Managing interns / juniors
- Managing stakeholders
- Trainings and workshops
- Conference attendance and speaking opportunities
- Open source projects
- Reading relevant books
After closing the gaps most of the way you need:
- open position - this is your responsibility to create one. If you talk about a promotion, you need to create a new position. Don’t offer something you don’t have
- plan the budget for the coming year with the promotion in mind
- tell HR 6 months ahead of the promotion - don’t suprise them!
- promotions should be done at fixed dates
- 2x a year, e.g. 1st Feb and 1st of August with a 90:10 split. In August only urgent promotions are considered.
- Those dates are only for formalities, discussions over the year are ongoing.
Salary
Salaries need to be based on a salary band. Each band has a minimum and maximum salary, e.g. from $A to $B. The band for the next role is from $C to $D. Bands can overlap.
There can be two dates for salary increases per year - often together with the promotion data.
A easy way for increasing salaries is giving a salary increase budget to the CTO, e.g. 10% depending on future revenue increases. The CTO then distributes the budget to department heads or team leads, e.g. 8%, 10%, 10%, 13%, 8%. The distribution is based on team performance, or needs (avg. in team to low, team progressed). Team leads then distribute salary increases to individuals based on performance according to their role descriptions.
